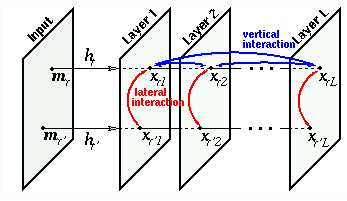
 The Competitive Layer Model (CLM) is a recurrent neural network architecture for dynamic feature binding and relaxation labeling, which was introduced by Helge Ritter in 1990. It can be used for various tasks in perceptual grouping, image segmentation, texture segmentation und classification. The network architecture consists of several topographically ordered layers within which lateral interactions control the binding of features into groups whereas competitve interactions between layers cause the segmentation and labeling of these groups. The stable states of the dynamics can be shown to be minima of a binding energy and implement proper groupings in the sense that each feature is uniquely assigned to a group.
The Competitive Layer Model (CLM) is a recurrent neural network architecture for dynamic feature binding and relaxation labeling, which was introduced by Helge Ritter in 1990. It can be used for various tasks in perceptual grouping, image segmentation, texture segmentation und classification. The network architecture consists of several topographically ordered layers within which lateral interactions control the binding of features into groups whereas competitve interactions between layers cause the segmentation and labeling of these groups. The stable states of the dynamics can be shown to be minima of a binding energy and implement proper groupings in the sense that each feature is uniquely assigned to a group.
read more »





















