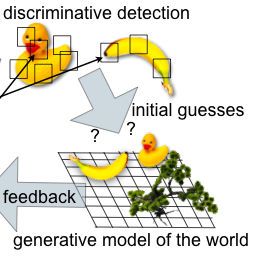
 The ultimate goal of biological vision systems is to infer knowledge about the outside world that is relevant for the system in order to interact with its environment. Therefore, it is not sufficient to just determine the category or the mere object identity. Many variables of interest must be estimated, for example the distance towards an object, the size, orientation, velocity or even such abstract variables like the mood of another animal. In this project we aim to extend existing invariant recognition approaches by using a new approach to hierarchical generative networks in order to implicitly represent (and learn) visual objects, and finally even scenes.
The ultimate goal of biological vision systems is to infer knowledge about the outside world that is relevant for the system in order to interact with its environment. Therefore, it is not sufficient to just determine the category or the mere object identity. Many variables of interest must be estimated, for example the distance towards an object, the size, orientation, velocity or even such abstract variables like the mood of another animal. In this project we aim to extend existing invariant recognition approaches by using a new approach to hierarchical generative networks in order to implicitly represent (and learn) visual objects, and finally even scenes.
read more »





















